Women’s reproductive health is often affected by complex conditions that can impact fertility, hormonal balance, and overall well-being. Two of the most common conditions are PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) and Endometriosis. Although they are often confused because of overlapping symptoms like irregular periods and infertility, they are entirely different in nature. In this blog, we will explore the differences between PCOS and Endometriosis, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments to help women understand these conditions better.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder in women that occurs when the ovaries produce higher-than-normal levels of male hormones (androgens). This imbalance disrupts ovulation and can cause multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
Key Causes of PCOS
-
Genetic factors and family history
-
Hormonal imbalance (especially excess androgens)
-
Insulin resistance leading to weight gain and metabolic problems
Common Symptoms of PCOS
-
Irregular periods or missed periods
-
Excessive hair growth (hirsutism)
-
Acne and oily skin
-
Weight gain and difficulty losing weight
-
Hair thinning or male-pattern baldness
-
Infertility due to lack of ovulation
What is Endometriosis?
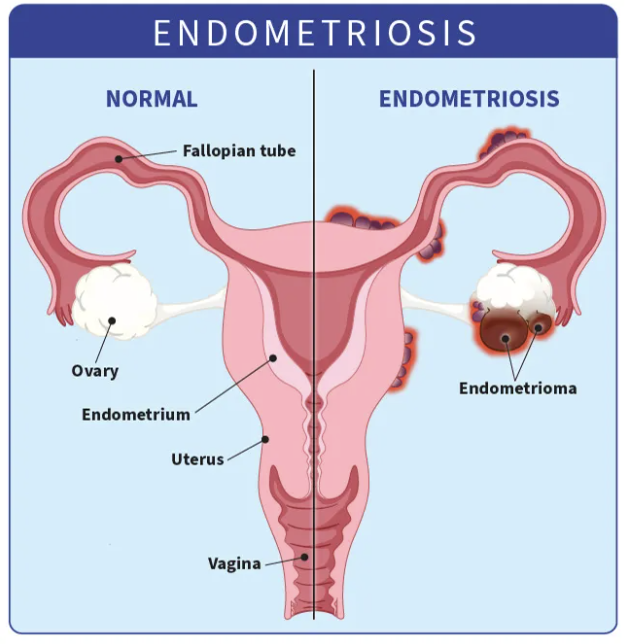
Endometriosis is a chronic gynaecological condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. This misplaced tissue causes inflammation, pain, and scar tissue formation.
Key Causes of Endometriosis
While the exact cause is unknown, possible reasons include:
-
Retrograde menstruation (menstrual blood flowing backward into the pelvis)
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Immune system dysfunction
-
Hormonal factors (estrogen dominance)
Common Symptoms of Endometriosis
-
Severe pelvic pain and cramping during periods
-
Heavy menstrual bleeding
-
Painful intercourse
-
Pain during urination or bowel movements
-
Infertility due to scarring and adhesions
PCOS vs Endometriosis: Key Differences
| Aspect | PCOS | Endometriosis |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Condition | Hormonal disorder | Structural/tissue disorder |
| Main Cause | Hormonal imbalance, excess androgens | Growth of uterine tissue outside uterus |
| Primary Symptoms | Irregular periods, acne, weight gain, hair growth | Painful periods, pelvic pain, infertility |
| Effect on Fertility | Lack of ovulation prevents pregnancy | Blocked fallopian tubes and scarring hinder conception |
| Pain Factor | Usually mild or absent | Severe pelvic pain and cramps |
| Treatment Focus | Regulating hormones, managing insulin resistance | Reducing pain, removing endometrial tissue |
Can You Have Both PCOS and Endometriosis?
Yes, some women may experience both PCOS and Endometriosis simultaneously. This makes diagnosis more complicated since both conditions can cause irregular cycles and infertility. Consulting a gynaecologist specializing in reproductive health is crucial for proper evaluation.
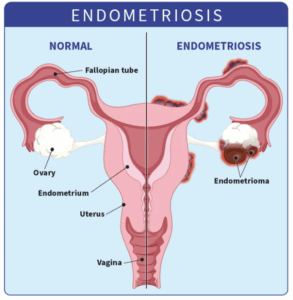
How PCOS and Endometriosis Affect Fertility
-
Women with PCOS often struggle with anovulation (failure to release eggs), which makes it difficult to conceive naturally.
-
Women with Endometriosis may have blocked fallopian tubes, scar tissue, and pelvic inflammation, all of which can interfere with egg fertilization and implantation.
Both conditions are leading causes of female infertility, but with early diagnosis and treatment, pregnancy is still possible.
Diagnosis of PCOS vs Endometriosis
PCOS Diagnosis
-
Ultrasound scan to detect cysts on ovaries
-
Blood tests for hormone levels (androgens, insulin, thyroid)
-
Medical history and symptoms evaluation
Endometriosis Diagnosis
-
Pelvic examination
-
Ultrasound and MRI scans to detect tissue growths
-
Laparoscopy (minor surgical procedure for confirmation)
Treatment Options for PCOS and Endometriosis
PCOS Treatment
-
Lifestyle changes: weight management, exercise, and diet
-
Medications for PCOS:
-
Birth control pills to regulate periods
-
Metformin for insulin resistance
-
Fertility drugs like Clomiphene for ovulation
-
-
Cosmetic treatments for acne and hair growth
Endometriosis Treatment
-
Pain management: NSAIDs for cramps
-
Hormonal therapy: birth control pills, progestins, GnRH agonists
-
Surgical options: laparoscopy to remove tissue growths and scar tissue
-
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) for women struggling with infertility
Lifestyle Management for Both Conditions
-
Balanced diet: Low-sugar, anti-inflammatory foods
-
Regular exercise: Helps with weight control and reduces pain
-
Stress management: Yoga, meditation, and relaxation techniques
-
Regular medical check-ups for early intervention
Conclusion
While PCOS and Endometriosis may share some symptoms, they are fundamentally different conditions. PCOS is primarily a hormonal imbalance, whereas Endometriosis involves abnormal tissue growth. Both conditions can affect fertility, but effective treatments are available.
If you experience irregular periods, pelvic pain, or infertility, it is important to consult a gynaecologist for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and increase chances of conception.