Women’s reproductive health has always been surrounded by curiosity, cultural beliefs, and unfortunately, a lot of myths and misconceptions. These myths often prevent women from seeking the right medical advice, maintaining good reproductive health, and making informed decisions about their bodies. With the help of modern medicine and expert gynaecologists, it’s important to separate facts from fiction.
In this blog, we’ll debunk the most common myths and provide accurate facts about women’s reproductive health.
Myth 1: Menstrual Irregularities Are Normal and Don’t Need Treatment
Fact: While slight variations in the menstrual cycle are common, consistently irregular periods, very heavy bleeding, or extremely painful cramps are not normal. These may indicate underlying conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or thyroid problems. Women experiencing such symptoms should consult a gynaecologist to identify the root cause and begin treatment early.
Myth 2: You Can’t Get Pregnant During Your Period
Fact: Though the chances of getting pregnant during menstruation are lower, it’s not impossible. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to 5 days, which means if ovulation happens shortly after a woman’s period, pregnancy can occur. Couples trying to avoid pregnancy should rely on proper contraceptive methods instead of depending on timing alone.
Myth 3: Contraceptives Cause Infertility
Fact: This is one of the most common contraception myths. Birth control pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), or implants do not cause infertility. Once a woman stops using them, her fertility usually returns to normal within a few weeks to months. However, fertility naturally declines with age, which may be wrongly attributed to long-term contraceptive use.
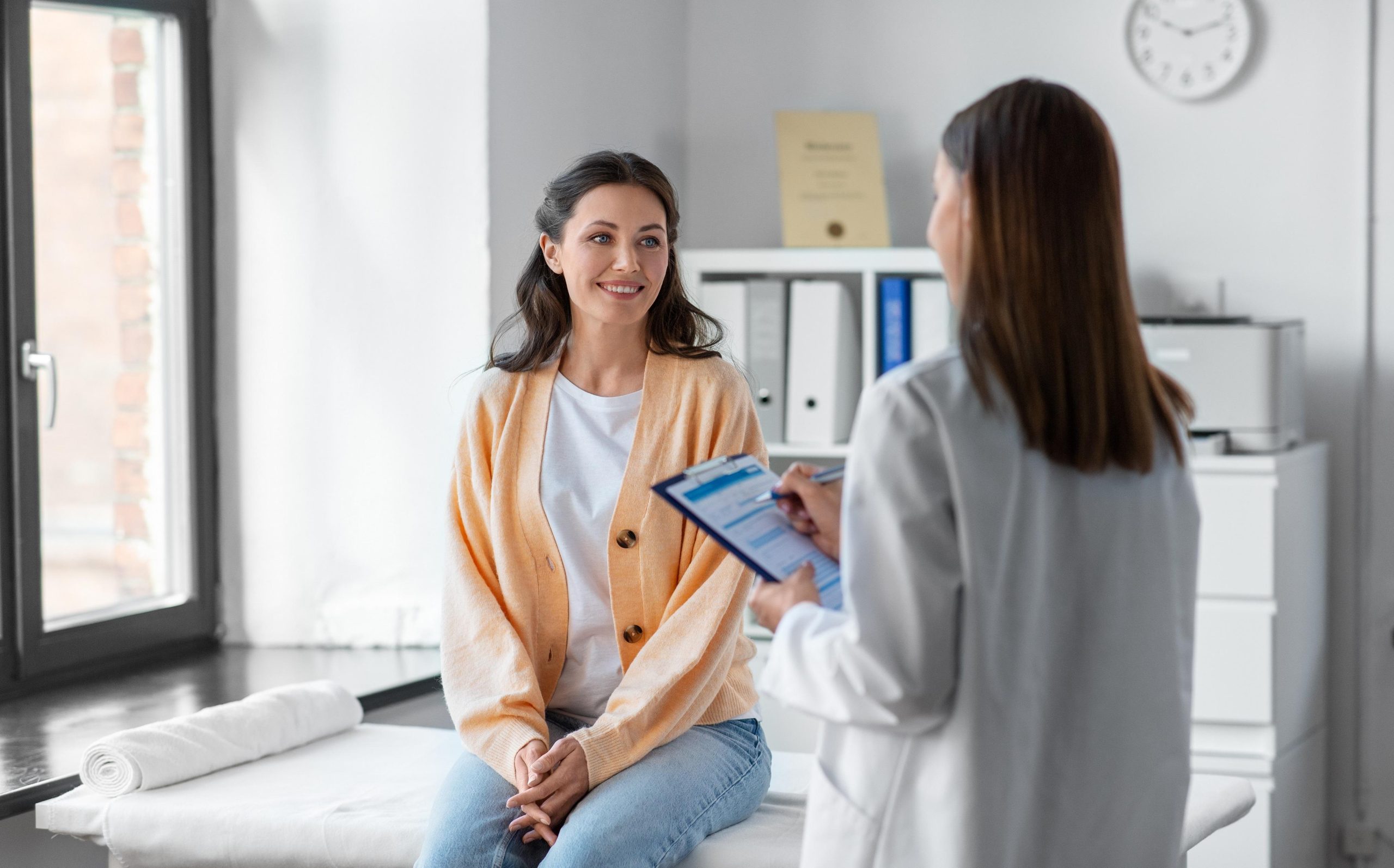
Myth 4: Pap Smear Tests Are Only Needed After Age 30
Fact: A Pap smear test is essential for detecting cervical cancer at an early stage. Women should start Pap smears at the age of 21, regardless of whether they are sexually active or not. Regular screenings every 3 years (or as advised by a doctor) play a critical role in maintaining women’s reproductive health and preventing serious complications.
Myth 5: Menopause Only Affects Fertility
Fact: Menopause is not just about the end of fertility. It can also lead to hormonal changes that affect bone health, heart health, metabolism, mental well-being, and sexual health. Symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness are also common. Consulting a gynaecologist for menopause management can help women cope with these changes more comfortably.
Myth 6: Vaginal Infections Always Mean Poor Hygiene
Fact: Not all vaginal infections are related to hygiene. Conditions like yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, or sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may occur due to hormonal imbalance, antibiotic use, or unprotected sexual contact. Maintaining proper intimate hygiene, wearing breathable cotton underwear, and visiting a gynaecologist for recurrent infections is important for long-term reproductive health.
Myth 7: Only Women With Multiple Partners Need STD Testing
Fact: Any sexually active woman can be at risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Even in monogamous relationships, there’s a possibility of infection if one partner is unknowingly carrying an STI. Regular STD screening is a crucial step in safeguarding reproductive health, preventing complications, and ensuring overall well-being.
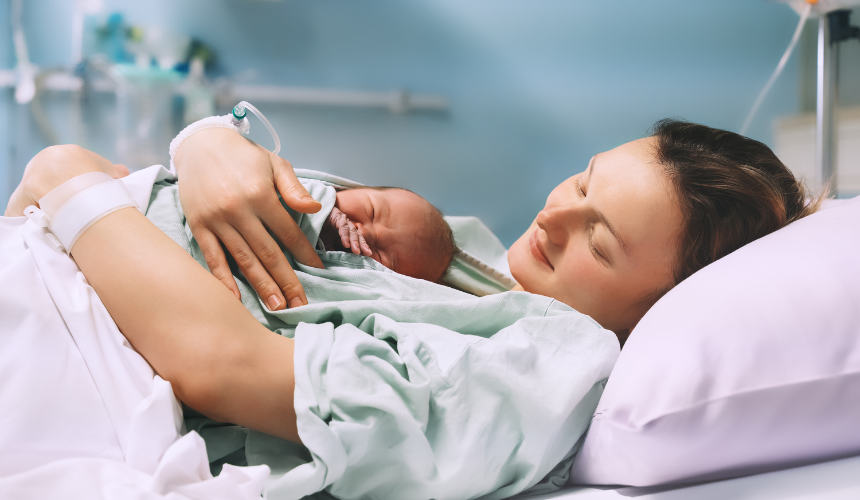
Myth 8: C-Section Deliveries Make Normal Delivery Impossible Later
Fact: Many women believe that once they have a C-section, they cannot have a vaginal delivery in future pregnancies. This is not true. Many women with a prior C-section can go through a Vaginal Birth After Cesarean (VBAC) depending on their medical history and the reason for the first C-section. Consulting an experienced obstetrician and gynaecologist is essential for safe delivery planning.
Myth 9: PCOS Means You Can Never Get Pregnant
Fact: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition that can affect ovulation and fertility, but it doesn’t mean pregnancy is impossible. With lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, fertility treatments like IUI or IVF, many women with PCOS successfully conceive and deliver healthy babies.
Myth 10: Women Don’t Need Gynaecological Check-Ups Unless They Are Pregnant
Fact: Regular gynaecology check-ups are important for women of all ages, even if they are not planning a pregnancy. These visits help in detecting early signs of ovarian cysts, fibroids, cancers, and infections. Preventive healthcare is as important as treatment, and timely check-ups save lives.
Tips to Maintain Good Reproductive Health
-
Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
-
Exercise regularly to regulate hormones and improve overall health.
-
Practice safe sex and use reliable contraceptive methods.
-
Schedule annual gynaecology check-ups for preventive care.
-
Manage stress, as it directly affects menstrual and reproductive health.
-
Stay aware of fertility health and consult a specialist if needed.
Final Thoughts
Women’s reproductive health should not be clouded by myths and misinformation. Believing in false claims can delay diagnosis, worsen conditions, and create unnecessary fear. Always rely on medical facts, consult a trusted gynaecologist, and stay informed about the latest advancements in women’s health care.
By debunking these common myths, women can take charge of their bodies, improve fertility, manage reproductive issues effectively, and lead healthier lives.