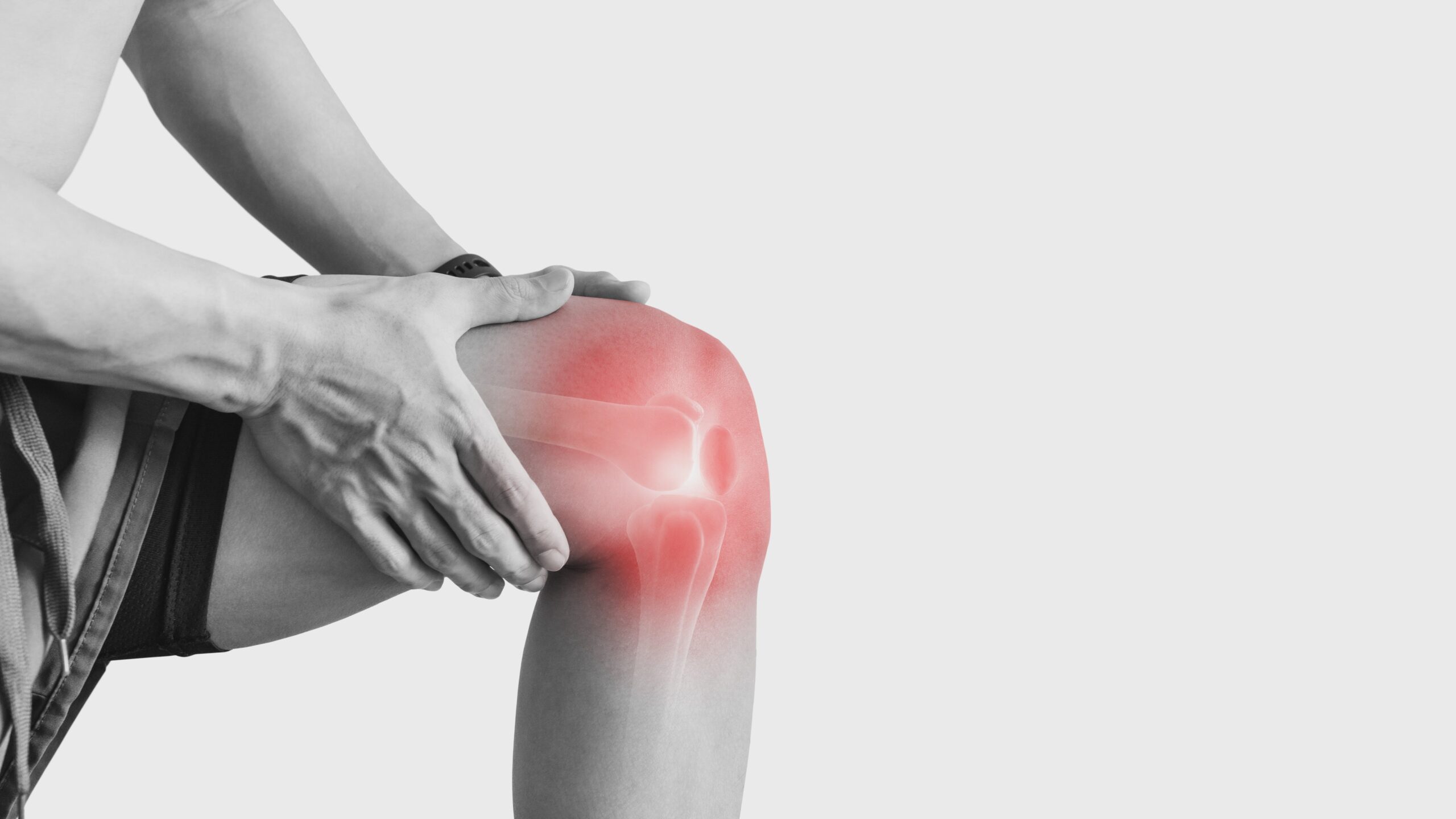
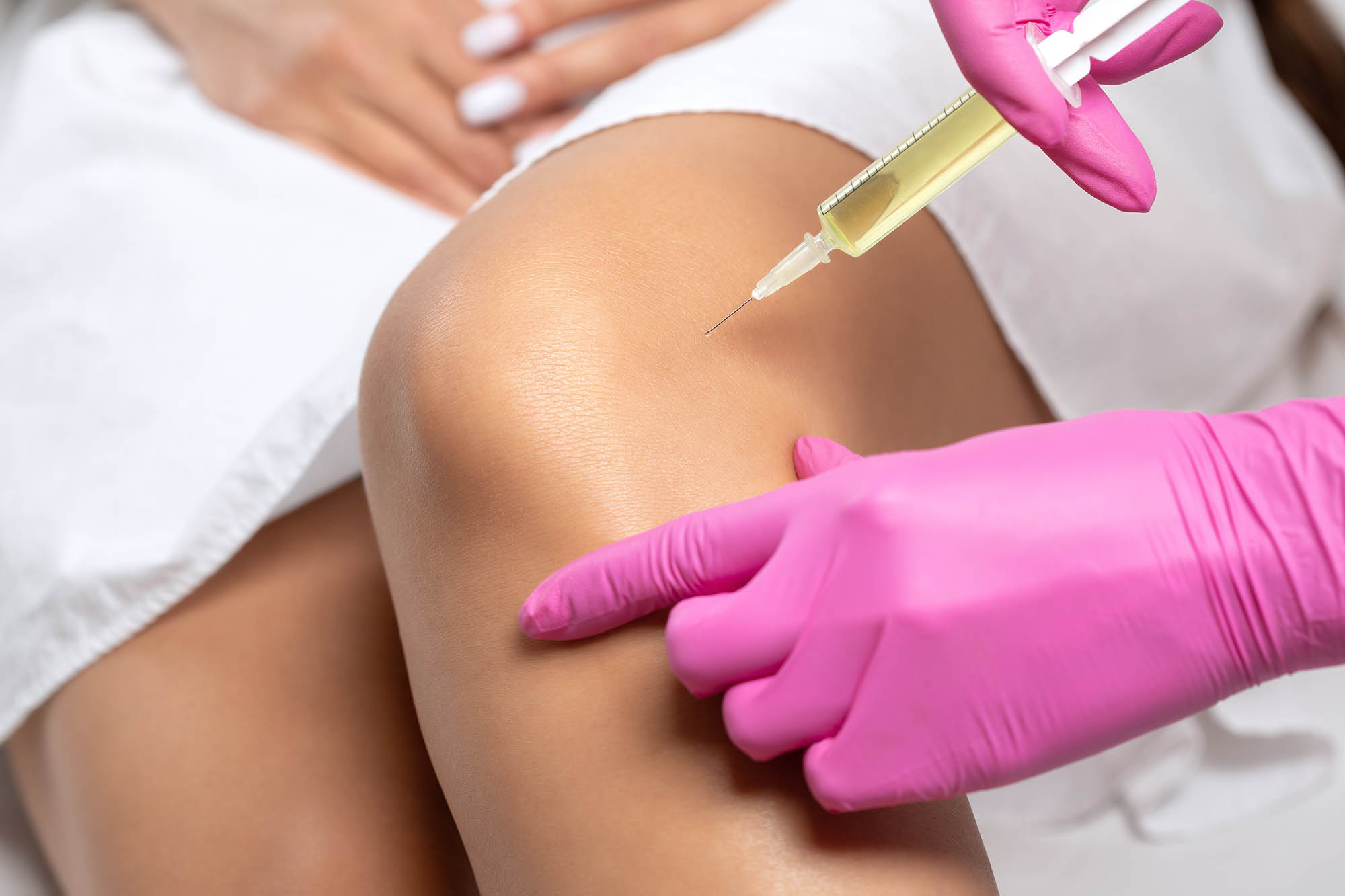
Joint pain is one of the most common health complaints that affects people of all ages. Whether it’s a dull ache in the knees, stiffness in the shoulders, or sharp pain in the hips, joint pain can significantly affect mobility and quality of life. It is not just an issue for the elderly; even young adults and athletes often suffer from painful joints due to injuries, lifestyle factors, or underlying medical conditions.
If you’re struggling with discomfort, understanding the causes of joint pain and exploring effective management options is the first step toward lasting relief. In this blog, we’ll discuss the most common reasons for joint pain, and how to manage it with home remedies, medical treatments, and lifestyle changes.
Common Causes of Joint Pain
1. Arthritis
The most common cause of joint pain is arthritis, which refers to inflammation in the joints. There are different types of arthritis:
-
Osteoarthritis (OA): Caused by wear and tear of the cartilage, often affecting older adults.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the joints, causing swelling and stiffness.
-
Gout: Caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, often leading to sudden and severe pain in the big toe, ankle, or knee.
Arthritis is one of the leading reasons people seek joint pain treatment from an orthopaedic doctor.
2. Injuries and Overuse
Sports injuries, falls, and accidents can lead to ligament tears, tendon injuries, or fractures, all of which cause joint pain. Even repetitive strain from daily activities or overuse in sports can lead to chronic pain in joints like the knee, elbow, or shoulder.
3. Bursitis
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. Bursitis occurs when these sacs become inflamed, often from repetitive motion or prolonged pressure, leading to pain in joints like the shoulder, hip, or knee.
4. Tendinitis
Tendinitis refers to inflammation of the tendons, the thick cords that attach muscles to bones. This condition is common among athletes and people who perform repetitive motions, resulting in shoulder pain, elbow pain, or knee pain.
5. Infections and Autoimmune Disorders
Certain infections like viral or bacterial infections can affect joints and cause pain. Autoimmune conditions such as lupus or psoriatic arthritis also trigger long-term joint inflammation and stiffness.
6. Other Causes
-
Poor posture
-
Excess body weight putting stress on knees and hips
-
Vitamin D or calcium deficiency
-
Sedentary lifestyle
How to Manage Joint Pain
The good news is that joint pain relief is possible with the right approach. Management depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and lifestyle factors.
1. Home Remedies for Joint Pain
Many people find relief with simple, effective remedies at home:
-
Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs reduces swelling, while heat pads ease stiffness.
-
Gentle Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and yoga help strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
-
Healthy Diet: Eating foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids supports bone and joint health.
-
Weight Management: Reducing excess body weight relieves stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
These home remedies for joint pain are particularly helpful for mild to moderate discomfort.
2. Physiotherapy for Joint Pain
Physiotherapy is one of the most effective non-surgical treatments for managing joint pain. A trained physiotherapist can design personalized exercises to strengthen the muscles around the joints, improve mobility, and reduce pain. This is highly recommended for people recovering from sports injuries, knee pain, or arthritis.
3. Medications
Doctors may prescribe:
-
Pain relievers (NSAIDs): To reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Corticosteroid injections: For severe cases of arthritis or joint swelling.
-
Supplements: Such as glucosamine, calcium, and vitamin D to improve joint and bone strength.
4. Advanced Orthopaedic Treatments
If non-surgical methods don’t provide enough relief, an orthopaedic doctor may recommend advanced treatments like:
-
Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to repair damaged cartilage or ligaments.
-
Joint Replacement Surgery: Commonly done for hips and knees when arthritis damage is severe.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: A regenerative treatment to promote healing of damaged tissues.
These advanced procedures are highly effective in providing long-term joint pain treatment.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Posture Correction: Maintaining good posture reduces strain on the spine, hips, and knees.
-
Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises like cycling, swimming, and stretching help maintain joint flexibility.
-
Stress Management: Stress can worsen inflammation. Practices like meditation and deep breathing improve overall well-being.
When to See a Doctor for Joint Pain
While mild joint pain can often be managed at home, you should consult the best orthopaedic doctor if:
-
Pain persists for more than a few weeks
-
Joints are visibly swollen or deformed
-
Pain is accompanied by fever or sudden redness
-
You experience difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, or performing daily activities
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further damage and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a common issue, but it should never be ignored. From arthritis and sports injuries to bursitis and tendinitis, the causes are varied, and so are the solutions. With a combination of home remedies, physiotherapy, medications, and advanced orthopaedic treatments, long-term relief is possible.
If you’re struggling with persistent joint pain, consult an orthopaedic specialist for a tailored treatment plan. Taking early steps can help restore mobility, improve bone and joint health, and get you back to living pain-free.